Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 200031, China
4 School of Science, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
Remote or standoff detection of greenhouse gases, air pollutants, and biological agents with innovative ultrafast laser technology attracts growing interests in recent years. Hybrid femtosecond/picosecond coherent Raman spectroscopy is considered as one of the most versatile techniques due to its great advantages in terms of detection sensitivity and chemical specificity. However, the simultaneous requirement for the femtosecond pump and the picosecond probe increases the complexity of optical system. Herein, we demonstrate that air lasing naturally created inside a filament can serve as an ideal light source to probe Raman coherence excited by the femtosecond pump, producing coherent Raman signal with molecular vibrational signatures. The combination of pulse self-compression effect and air lasing action during filamentation improves Raman excitation efficiency and greatly simplifies the experimental setup. The air-lasing-assisted Raman spectroscopy was applied to quantitatively detect greenhouse gases mixed in air, and it was found that the minimum detectable concentrations of CO2 and SF6 can reach 0.1% and 0.03%, respectively. The ingenious designs, especially the optimization of pump-seed delay and the choice of perpendicular polarization, ensure a high detection sensitivity and signal stability. Moreover, it is demonstrated that this method can be used for simultaneously measuring CO2 and SF6 gases and distinguishing 12CO2 and 13CO2. The developed scheme provides a new route for high-sensitivity standoff detection and combustion diagnosis.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9761458

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
2 Department of Physics, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 School of Science, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, China
4 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics and CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Shanghai 201800, China
5 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
Molecular ions, produced via ultrafast ionization, can be quantum emitters with the aid of resonant electronic couplings, which makes them the ideal candidates to study strong-field quantum optics. In this work, we experimentally and numerically investigate the necessary condition for observing a collective emission arising from macroscopic quantum polarization in a population-inverted gain system, uncovering how the individual ionic emitters proceed into a coherent collection within hundreds of femtoseconds. Our results show that for a relatively high-gain case, the collective emission behaviors can be readily initiated for all the employed triggering pulse area. However, for a low-gain case, the superradiant amplification is quenched since the building time of macroscopic interionic quantum coherence exceeds the dipole dephasing time, in which situation the seed amplification and free induction decay play an essential role. These findings not only clarify the contentious key issue regarding to the amplification mechanism of lasing but also show the unique characteristics of ultrashort laser-induced amplification in a molecular ion system where both the microscopic and macroscopic quantum coherence might be present.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(10): 10002046
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院超强激光科学卓越创新中心, 上海 201800
3 华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室, 上海 200062
空气激光是以空气为增益介质产生的相干辐射,具有高准直度、高相干性、高强度以及自由空间传输等优点,为远程探测提供了全新的技术途径。同时,空气激光是强场超快激光与空气中的原子分子相互作用的结果,蕴含了新颖而丰富的强场物理效应。综述了空气激光近年来的主要研究进展。首先介绍了三类空气激光的产生途径及基本特征,然后从氮气离子激光的增益机制以及量子相干性两个层面阐述了空气激光所蕴含的新物理效应,并讨论了空气激光在远程探测中的应用,最后总结了空气激光研究的意义,展望了该方向面临的机遇与挑战。
超快光学 空气激光 强场激光物理 远程探测
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 School of Science, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
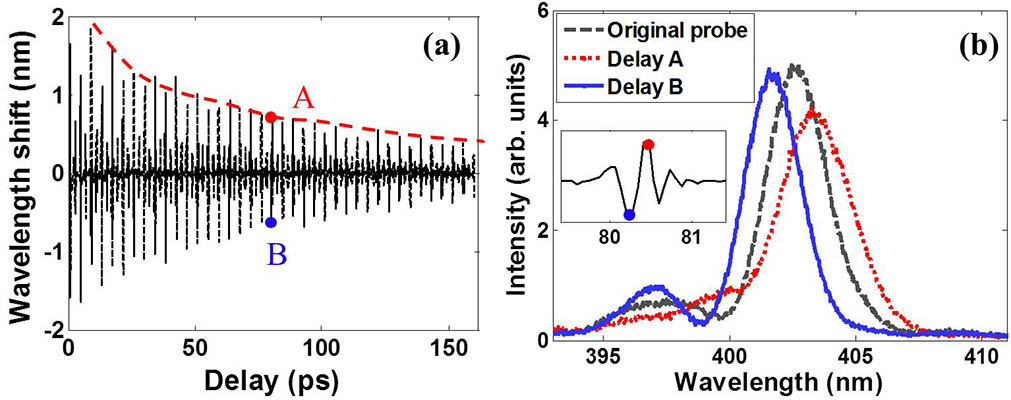
We report on an experimental investigation on the dynamic decoherence process of molecular rotational wavepackets during femtosecond laser filamentation based on time-dependent mean wavelength shifts of a weak probe pulse. Details of periodic revival structures of transient alignment can be readily obtained from the measured shifted spectra due to the periodic modulation of the molecular refractive index. Using the method, we measured decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets in N2 and O2 under different experimental conditions. Our results indicate that decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets are primarily determined by the relative population of rotational states in the wave packet and intermolecular collisions, rather than the focusing intensity.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 300.6530 Spectroscopy, ultrafast Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(12): 120201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, East China Jiatong University, Nanchang 330013, China
2 School of Science, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
3 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
4 School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
We experimentally investigate the generation of above-threshold harmonics completely from argon atoms on an excited state using mid-infrared femtosecond laser pulses. The highly nonlinear dependences of the observed signal on the pulse energy and polarization of the probe laser pulses indicate its nonperturbative characteristic.
above-threshold harmonics excited state mid-infrared femtosecond laser High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(4): 04000e26

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
We experimentally demonstrate N2+ lasing actions at the wavelengths of 353.3, 353.8, and 354.9 nm using a circularly polarized femtosecond laser. The three laser lines correspond to the B2Σu+(v′=5,4,3)→X2Σg+(v=4,3,2) transitions, respectively. Particularly, we reveal the pressure-dependent gain dynamics of these lasing actions from highly excited vibrational states with a pump–probe scheme. Our experimental results confirm that electron collisional excitation plays an important role in the establishment of a population inversion of N2+ lasing at these wavelengths.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 320.7150 Ultrafast spectroscopy 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(5): 050201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Graduate University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We theoretically propose a new method for generating intense isolated attosecond pulses during high-order harmonic generation (HHG) process by accurately controlling electron motion with a two-color laser field, which consists of an 800-nm, 4-fs elliptically polarized laser field and a 1400-nm, ~43-fs linearly polarized laser field. With this method, the supercontinua with a spectral width above 200 eV are obtained, which can support a ~15-as isolated pulse after phase compensation. Classical and quantum analyses explain the controlling effects well. In particular, when the pulse duration of the 800-nm laser field increases to 20-fs, sub-100-as isolated pulses can be obtained even without any phase compensation.
单个阿秒脉冲 高次谐波产生 双色场 190.4160 Multiharmonic generation 340.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) 020.2649 Strong field laser physics Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(4): 041901





